Table1 : Characteristics of different types of viral tools used for sparse highlighting labeling
| Virus type | Labeling type | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
Vesicularstomatitis Virus, VSV |
Local labeling | Broad host range, fast and high-brightness labeling, and high cytotoxicity |
|
Semliki forest virus, SFV |
Local labeling | Broad host range, fast and high-brightness labeling, and high cytotoxicity |
|
Adeno-associated Virus, AAV |
Local labeling | Broad host range, fast and high-brightness labeling, and high cytotoxicity |
|
Rabies virus, RV |
Retrograde labeling or retrograde trans-monosynaptic labeling | Broad host range, retrograde labeling and cytotoxicity in long-term infections |
|
Canine adenovirus, CAV |
Retrograde labeling | Low cytotoxicity and achievable cell type specific labeling/td> |
At present, virus tools have been widely used in neural tracing research, among them, AAV, SFV, RV and VSV are often used for sparse labeling. These virus were injected into the specific brain area, and after the reporter gene was expressed for a certain time, optical imaging analysis and FMOST could be combined to realize the sparse labeling of neurons in a specific brain area.
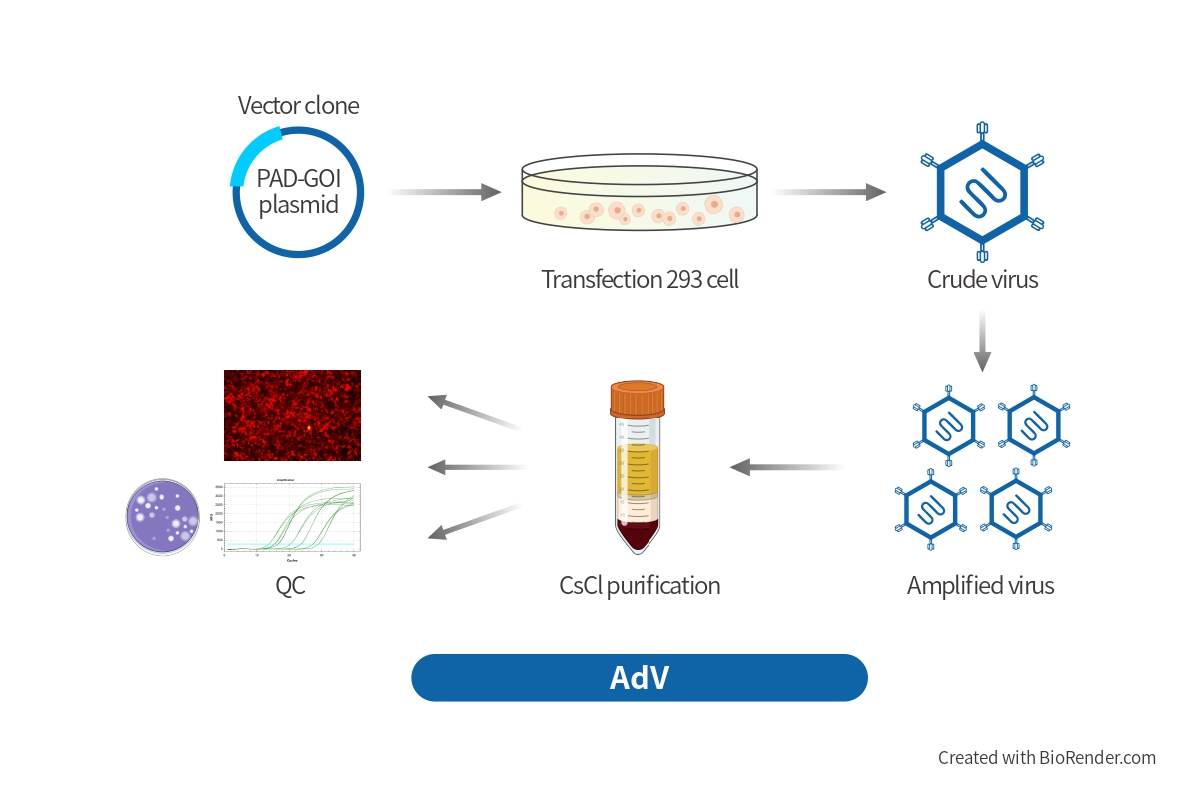
● Sparse labeling based on the single virus system.
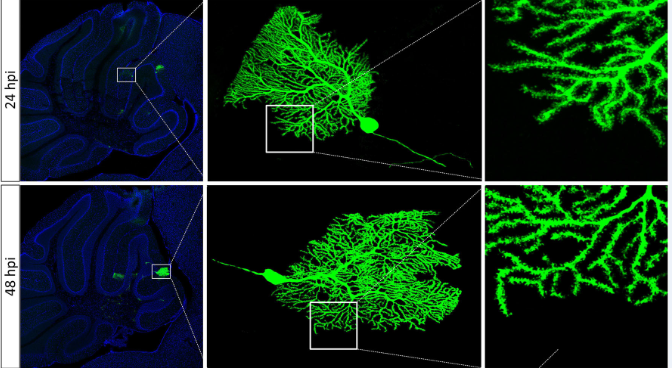
VSV, SFV, RV and CAV have a high efficiency of infection. A small amount of infection can express high abundance of fluorescent protein. Therefore, rapid, sparse and bright cell labeling of the complete morphology of local neurons can be achieved by reducing the viral titer. These tools enables fast bright cell labeling but is cytotoxic, so it is suitable for sparse labeling of local dendrites but not for long-term projection.
●Sparse labeling based on TRE leakage combined with tTA/TRE.
This labeling method can be used for post-division neurons, and the labeling duration can be up to 8 months, but it is not suitable for labeling the dividing cells, during which the vector is diluted and the fluorescence intensity is also affected.
● Sparse labeling based on Cre/FLP recombinase.
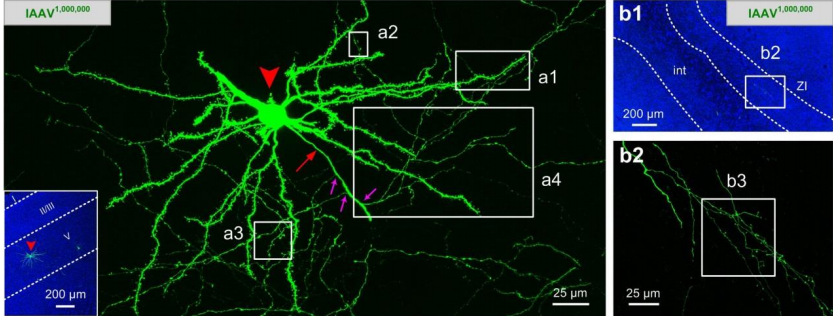
The method controls the number of bright neurons in the target area between 10- 50 by adjusting the injection volume of the virus. The cells labeled with this method are exquisitely shaped and can trace the morphology of the whole brain to a certain extent.
● Sparse labeling based on recombinase system-dependent copackaging strategy
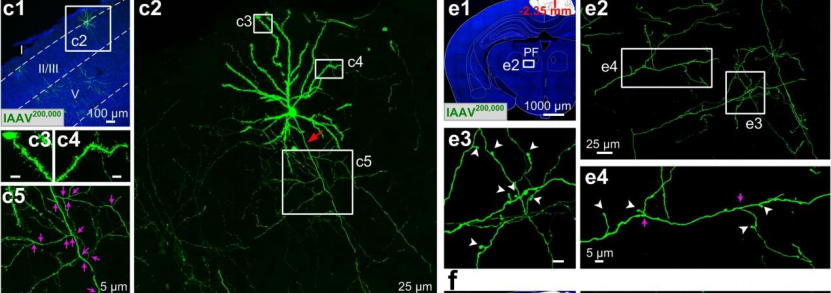
The recombinase system-dependent (including Cre-lox/Flp-FRT ) viral copackaging strategy improve mutual inhibition and enhance compatibility among different rAAVs. And the author found that it was ~5-fold and over 10-fold more sensitive than the mixture of independently packaged rAAVs, enabling us to capture massive morphological details of individual neurons.
BrainVTA has extensive experience in sparse labeling, and could offer optimum experimental conditions according to your requirements. If you have any need, just email us at sales@brainvta.com.
References
- Elife. 2016 Jan 20;5:e10566. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10566.
A platform for brain-wide imaging and reconstruction of individual neurons. - Nature. 2012 Dec 13;492(7428):247-51. doi: 10.1038/nature11601.
Nonlinear dendritic integration of sensory and motor input during an active sensing task. - Sci Rep.2016 Oct 24;6:35747. doi: 10.1038/srep35747.
Supernova: A Versatile Vector System for Single-Cell Labeling and Gene Function Studies in vivo. - .Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 8;7:43915. doi: 10.1038/srep43915.
Genetically-directed Sparse Neuronal Labeling in BAC Transgenic Mice through Mononucleotide Repeat Frameshift. - Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220(3):1369-79. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0730-z.
An anterograde rabies virus vector for high-resolution large-scale reconstruction of 3D neuron morphology. - J Comp Neurol. 2009 Oct 20;516(6):456-81. doi: 10.1002/cne.22131.
Viral strategies for studying the brain, including a replication-restricted self-amplifying delta-G vesicular stomatis virus that rapidly expresses transgenes in brain and can generate a multicolor golgi-like expression - 7. bioRxiv preprint first posted online Jul. 17, 2019; doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/705772
Recombinase system-dependent copackaging strategy for highly efficient neurocircuit tracing.